Your online security depends on more than just a password. Imagine if a simple code wasn’t enough to protect your personal data or business information from hackers.
Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a powerful layer of defense that could stop cyber threats before they reach you. If you want to keep your accounts truly safe and avoid costly breaches, understanding how MFA works is key. Keep reading to discover why this security step matters and how you can use it to protect what’s yours.

Credit: www.uscybersecurity.net
Why Mfa Matters
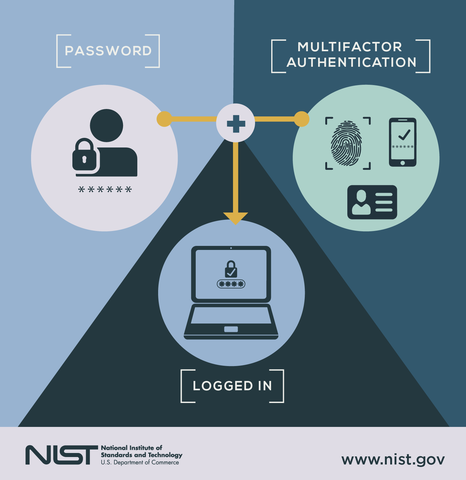
Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection for online accounts. It helps keep hackers out by requiring more than just a password. This simple step can save users from many cyber threats. Understanding why MFA matters helps people take online security seriously.
Common Cyber Threats
Hackers use many tricks to steal passwords. Phishing emails trick users into giving login details. Malware can capture keystrokes or steal saved passwords. Data breaches expose millions of passwords at once. Cybercriminals try to access accounts for money or information.
Limitations Of Passwords
Passwords alone are not strong enough. Many people use weak or repeated passwords. Passwords can be guessed or stolen easily. Users often share passwords or write them down. A single password can open many accounts if reused.
Mfa Impact On Security
MFA requires a second step to verify identity. This could be a code sent to a phone or a fingerprint scan. Even if a password is stolen, the account stays safe. MFA reduces the risk of unauthorized access. It makes online accounts much harder to hack.
Types Of Mfa Methods
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) uses different ways to confirm your identity. It adds layers of security to protect your accounts. Various MFA methods exist, each with unique features and benefits. Understanding these types helps you pick the right one for your needs.
Sms And Email Codes
This method sends a code to your phone or email. You enter this code after typing your password. It is easy to use and widely available. But it depends on your mobile or internet connection. Sometimes, codes can be intercepted by hackers.
Authenticator Apps
Apps like Google Authenticator generate time-based codes. These codes change every 30 seconds. You use the app to get a code when logging in. It works without internet once set up. This method is safer than SMS or email codes.
Biometric Verification
Biometrics use your physical traits to verify identity. Common examples include fingerprints and facial recognition. It is quick and hard to fake. Many smartphones and laptops have built-in biometric sensors. This method adds strong protection without extra effort.
Hardware Tokens
Hardware tokens are small devices that create login codes. You carry them and press a button to get a code. Some connect via USB or Bluetooth to your device. They do not rely on internet or phone networks. Hardware tokens offer very high security for sensitive accounts.
Implementing Mfa
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) boosts security by requiring more than one proof of identity. It helps protect accounts from unauthorized access. Careful planning is needed to choose and set up the right MFA system.
Choosing The Right Method
Select an MFA method that fits your security needs and users. Common options include text messages, authentication apps, or hardware tokens. Authentication apps are safer than text messages. Hardware tokens offer strong protection but cost more. Balance security and ease of use.
Integration With Existing Systems
Check if the MFA solution works with current software and hardware. It should support your operating systems and applications. Smooth integration avoids disruptions in daily work. Test MFA on a small group before full rollout. This step ensures compatibility and fixes issues early.
User Experience Considerations
Keep the MFA process simple for users. Complicated steps may cause frustration and reduce adoption. Provide clear instructions and support. Allow backup options in case of lost devices. A good user experience encourages consistent use of MFA.

Credit: corsicatech.com
Mfa In Different Environments
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) plays a key role across various environments. It adds layers of security that protect sensitive information. Different settings use MFA in unique ways to fit their needs. Understanding these differences helps secure your digital life better.
Corporate Networks
Corporate networks store critical business data. MFA helps prevent unauthorized access to these systems. Employees log in using passwords plus a second factor. This could be a code sent to their phone. It reduces risks from stolen passwords or phishing attacks. Strong MFA is essential for protecting company secrets.
Cloud Services
Cloud services hold data and applications online. MFA protects accounts from hackers trying to steal cloud credentials. Users enter their password and a verification code from an app. This extra step blocks many cyber threats. It keeps cloud data safer and helps maintain trust.
Personal Accounts
Personal accounts include email, social media, and banking. MFA stops strangers from accessing private information. Most services offer simple MFA options like text codes or authenticator apps. Users add a second step after their password. This small effort greatly improves account security.
Challenges And Limitations
Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) strengthens security but also faces some challenges. Understanding these limits helps to use MFA better.
User Resistance
Many users find MFA steps slow or annoying. They may skip or avoid extra verification. This resistance can weaken security efforts. Training and clear communication help reduce user pushback.
Technical Issues
MFA systems can face technical problems. Users may lose access to their second factor, like phones or tokens. Network outages can block verification codes. These issues cause login delays and frustration.
Bypassing Mfa Risks
Some attackers find ways to bypass MFA. Phishing or social engineering tricks can steal codes. Malware can intercept second-factor data. No system is completely foolproof, so vigilance is necessary.
Credit: dpsnews.utah.gov
Future Of Mfa
The future of Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) holds many changes. It will become smarter and easier to use. Security will improve as new technologies enter the scene. Users will enjoy faster access without losing safety.
Advances in technology make MFA more reliable. Developers focus on reducing password use and adding new verification methods. This helps protect against hacking and fraud. The future promises a mix of strong security and user convenience.
Advancements In Biometrics
Biometric technology will improve greatly. Fingerprint scanners will become faster and more accurate. Face and iris recognition will work better in different lighting. New methods like vein or heartbeat scanning may appear. Biometrics will offer a secure way to confirm identity without passwords.
Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless systems will grow popular. Users will log in using devices or biometrics only. This removes weak or reused passwords from the process. It cuts risks from stolen or guessed passwords. Simple actions like tapping a phone or scanning a face will replace typing passwords.
Ai And Behavioral Analysis
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will help detect unusual user behavior. It learns normal patterns like typing speed or mouse movements. AI spots changes that may mean fraud or hacking. This adds a hidden layer of security. Behavioral analysis can stop threats before damage happens.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Multi Factor Authentication In Cyber Security?
Multi factor authentication (MFA) is a security process requiring users to provide two or more verification factors. It enhances protection by combining something you know, have, or are, reducing unauthorized access risks in cyber security.
How Does Mfa Improve Cyber Security Protection?
MFA adds extra verification layers beyond passwords. It requires multiple forms of identity proof, making it harder for attackers to breach accounts. This significantly lowers the chances of cyber attacks and identity theft.
Which Factors Are Commonly Used In Mfa?
Common MFA factors include passwords, mobile device codes, biometrics like fingerprints, and hardware tokens. These diverse methods ensure stronger security by verifying user identity through multiple independent means.
Is Mfa Difficult To Implement For Businesses?
Implementing MFA is straightforward with many user-friendly tools available. Most solutions integrate smoothly with existing systems, enhancing security without complicating user access or requiring extensive technical knowledge.
Conclusion
Multi-factor authentication adds strong protection to your online accounts. It uses more than one step to verify your identity. This extra layer helps stop hackers from gaining access. Many cyber threats rely on weak passwords alone. Using MFA makes it harder for attackers to succeed.
It is simple to set up and use on most devices. Stay safe by enabling MFA wherever possible today. Protect your data and privacy with this easy security step. Don’t leave your accounts open to risks. Multi-factor authentication is a smart choice for better cyber safety.





